Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 22)
W
White Balance:
Automatic white balance, it is often possible to choose between "daylight:, "overcast:" and "neon light" for even true colors or on the other hand create a different, striking effect.
Wide Angle Converter:
Lens attachment that reduces the focal length. (See also Macro converter, tele converter).
WWW:
World Wide Web. Currently the most popular service offered through the internet. The WWW provides the possibility to transmit files with multimedia contents (text, sound. picture)
Extended Graphics Array. A graphics Standard developed by IBM, which allows the display of 1024x768 pixels with upto 65,535 colors.
Y
Yahoo:
Well known internet search engine and mail services provider.
Z
 ZIP:
ZIP:
File format used for data compression.
![="Zoom]()
Zoom Lens:
Lens with a manually or a mechanically adjustable focal length.
Grab also »
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V
White Balance:
Automatic white balance, it is often possible to choose between "daylight:, "overcast:" and "neon light" for even true colors or on the other hand create a different, striking effect.
Wide Angle Converter:
Lens attachment that reduces the focal length. (See also Macro converter, tele converter).
WWW:
World Wide Web. Currently the most popular service offered through the internet. The WWW provides the possibility to transmit files with multimedia contents (text, sound. picture)
X
XGA:Extended Graphics Array. A graphics Standard developed by IBM, which allows the display of 1024x768 pixels with upto 65,535 colors.
Y
Yahoo:
Well known internet search engine and mail services provider.
Z

File format used for data compression.
Zoom Lens:
Lens with a manually or a mechanically adjustable focal length.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V
Labels:
Education,
LifeStyle,
Photography,
Technology
Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 21)
V
VGA:
Video Graphics Array. Refers to a display with a resolution of 640x 480 pixels.
VGA:
Video Graphics Array. Refers to a display with a resolution of 640x 480 pixels.
Video Output:
Interface that connect a digital camera with a TV or Video recorder.
Video CCD:
Describes a CCD specially developed for television and video, also used in digital still cameras.
Virus:
Describes a part of a computer program that usually causes damage or destruction of software and/or data.
Overview:
Labels:
Education,
LifeStyle,
Photography,
Technology
Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 20)
U
UART:
Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter. Set of chips in a computer regulating data flow over the serial interface.
Unsharp Masking:
Often abbreviated USM. Describes an image focusing process. The quality of the result depends on the characteristics of the algorithm used.
Update:
An updated version of a software program.
Upgrade:
A new improved version of hardware of software that is already available.
URL:
Unified Resources Locator. Address system for internet sites.
USB:
The Universal Serial Bus is probably going to replace the series and parallel interface. USB enables the effortless connection of peripheral devices without the need to install cards into the computer or reconfigure parts of the operating system. The most important advantages are: the support to Plug and Play. hot plugging, automatic configuration of external devices upon connection (no re-start necessary), faster data transfer (up to 12 Mbps), and the possible operation of up to 127 devices from a single port.
Utility:
A program that performs special task for the operating system, for example: file administration, controlling a digital camera, a CD-ROM drive or printer.
UXGA:
Ultra Extended Graphics Array. This refers to images with a resolution of 1600 x 1280 pixels. (See also SVGA, SXGA. VGA, XGA)
Grab also »
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, V, W-Z
UART:
Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter. Set of chips in a computer regulating data flow over the serial interface.
Unsharp Masking:
Often abbreviated USM. Describes an image focusing process. The quality of the result depends on the characteristics of the algorithm used.
Update:
An updated version of a software program.
Upgrade:
A new improved version of hardware of software that is already available.
URL:
Unified Resources Locator. Address system for internet sites.
USB:
The Universal Serial Bus is probably going to replace the series and parallel interface. USB enables the effortless connection of peripheral devices without the need to install cards into the computer or reconfigure parts of the operating system. The most important advantages are: the support to Plug and Play. hot plugging, automatic configuration of external devices upon connection (no re-start necessary), faster data transfer (up to 12 Mbps), and the possible operation of up to 127 devices from a single port.
Utility:
A program that performs special task for the operating system, for example: file administration, controlling a digital camera, a CD-ROM drive or printer.
UXGA:
Ultra Extended Graphics Array. This refers to images with a resolution of 1600 x 1280 pixels. (See also SVGA, SXGA. VGA, XGA)
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, V, W-Z
Labels:
Education,
LifeStyle,
Photography,
Technology
Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 19)
T
True Color:
Describes the colour output on a monitor or printer. Requires at least 16 million colour nuances.
Tele Converter:
Lens attachment that extends the focal length.
TFT:
Thin flim technology. Currently the highest quality of color LC-displays. TFT dispalys are used in notebooks as well as in digital cameras.Thumbnail:
The miniature representation of a digital image that usually serves as a preview function in image editing program.
TIFF:
Tagged Image File Format. A specific, high quality file format used for the storage of digitized images.
TTL metering:
Through The Lens Metering.
Twain Driver:
Technology Without An Interesting Name. Allows the transfer of scans or digital photos into image editing programs.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, U, V, W-Z
Labels:
Education,
LifeStyle,
Photography,
Technology
Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 18)
S
Scanner:
The process of reading information (picture, graphics and text) through the use of a scanner.
Scanner:
A device used to digitized printed information (picture, graphics and text).
SCSI:
Small Computer System Interface. A general interface standard used, for example, to connect external storage devices or scanners with a computer. It is necessary to differentiate between SCSI I, SCSI II and SCSI III.
Fig shows a icon/logo that used for SCSI.
Search Engine:
Helps catalogue and find the huge amount of information available on the internet. Such as Google (no 1 giant search engine), Yahoo, Altavista etc
SECAM:
Sequential Couleur Avec Memoire. It is a analog television standard first used in French. Also used in former East Bloc countries.
Self-Timer:
A function that delays the opening of the shutter. This ensures vibration-free operation during long exposure times and enables the photographer to get into the picture.
Sequence Mode:
Several shots are taken automatically in a row. (see Quick shooting mode)
Serial Interface:
Also called RS232C or RS422 interface. An interface which allows peripheral devices such as a mouse, modem and certain digital cameras to be connected to the computer. Data is transferred serially, which means bit by bit, one piece after another, via a connection cable.
Server:
The main computer in a network, responsible for the management/ regulation of all other computers.
Shooting Range:
The range in which a camera is able to capture sharp, focused images.
SHQ Resolution:
Super High Quality Resolution. A very high resolution digital photo.
SIMM:
Single In-line Memory Module. A common type of plug-in RAM memory modules for personal computers.
Single Lens Reflex Camera:
Camera type that directs the image coming in through the lens up unto the viewfinder by means of a mirror. When the shutter is released the mirror swings up to allow light on the image plane. For fast sequence shooting and to reduce vibrations, some SLR optical systems use a beam splitter (prism) instead of the quick return swinging mirror. The picture seen through the viewfinder is almost 100% identical to the resulting photo.
Slot:
Expansion interface in computers, notebooks and other devices. Expansion cards, e.g. PC Cards, can be plugged in here to increase performance, capacity or the capabilities of the device.
Spot Metering:
Exposure metering method whereby the exposure reading is taken from the center of the frame. This is often used when working with backlight.
SRAM:
Static RAM. A special type of RAM that, due to its speed, is particularly suited tasks where time is critical factor.
SVGA:
Super Video Graphics Array. Refers to a display screen, resolution of more than 800x600 pixels. (See also SXGA, VGA, UXGA, XGA)
SXGA:
Super Extended Graphics Array. Describes a resolution from 1280 x 1024 image.
SSFDC:
Solid State Floppy Disc Card.
Subtractive Color Mixing:
A special method for the production of color prints that involves layering the colours cyan, magenta, yellow and black in appropriate proportions, to produce the required colours.
Grab also »
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, T, U, V, W-Z
Scanner:
The process of reading information (picture, graphics and text) through the use of a scanner.
Scanner:
A device used to digitized printed information (picture, graphics and text).
SCSI:
Small Computer System Interface. A general interface standard used, for example, to connect external storage devices or scanners with a computer. It is necessary to differentiate between SCSI I, SCSI II and SCSI III.
Fig shows a icon/logo that used for SCSI.
Search Engine:
Helps catalogue and find the huge amount of information available on the internet. Such as Google (no 1 giant search engine), Yahoo, Altavista etc
SECAM:
Sequential Couleur Avec Memoire. It is a analog television standard first used in French. Also used in former East Bloc countries.
Self-Timer:
A function that delays the opening of the shutter. This ensures vibration-free operation during long exposure times and enables the photographer to get into the picture.
Sequence Mode:
Several shots are taken automatically in a row. (see Quick shooting mode)
Serial Interface:
Also called RS232C or RS422 interface. An interface which allows peripheral devices such as a mouse, modem and certain digital cameras to be connected to the computer. Data is transferred serially, which means bit by bit, one piece after another, via a connection cable.
Server:
The main computer in a network, responsible for the management/ regulation of all other computers.
Shooting Range:
The range in which a camera is able to capture sharp, focused images.
SHQ Resolution:
Super High Quality Resolution. A very high resolution digital photo.
SIMM:
Single In-line Memory Module. A common type of plug-in RAM memory modules for personal computers.
Single Lens Reflex Camera:
Camera type that directs the image coming in through the lens up unto the viewfinder by means of a mirror. When the shutter is released the mirror swings up to allow light on the image plane. For fast sequence shooting and to reduce vibrations, some SLR optical systems use a beam splitter (prism) instead of the quick return swinging mirror. The picture seen through the viewfinder is almost 100% identical to the resulting photo.
Slot:
Expansion interface in computers, notebooks and other devices. Expansion cards, e.g. PC Cards, can be plugged in here to increase performance, capacity or the capabilities of the device.
Spot Metering:
Exposure metering method whereby the exposure reading is taken from the center of the frame. This is often used when working with backlight.
SRAM:
Static RAM. A special type of RAM that, due to its speed, is particularly suited tasks where time is critical factor.
SVGA:
Super Video Graphics Array. Refers to a display screen, resolution of more than 800x600 pixels. (See also SXGA, VGA, UXGA, XGA)
SXGA:
Super Extended Graphics Array. Describes a resolution from 1280 x 1024 image.
SSFDC:
Solid State Floppy Disc Card.
Subtractive Color Mixing:
A special method for the production of color prints that involves layering the colours cyan, magenta, yellow and black in appropriate proportions, to produce the required colours.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, T, U, V, W-Z
Labels:
Education,
LifeStyle,
Photography,
Technology
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Blog Archive
-
▼
2011
(178)
-
▼
November
(17)
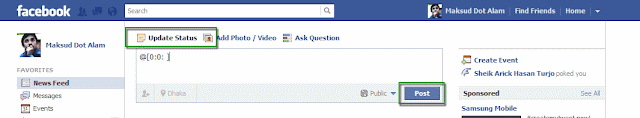
- How to post Blank Status in Facebook
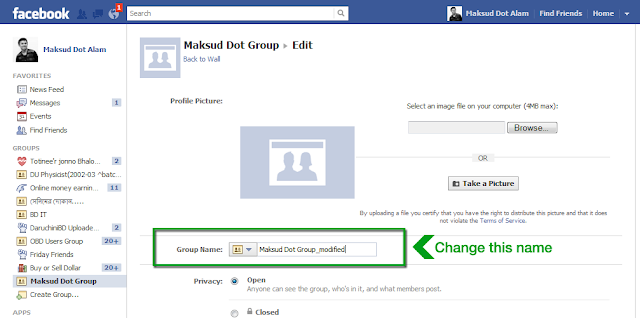
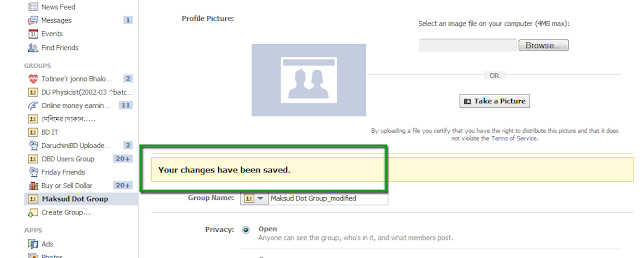
- How to rename Facebook Group Name
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 22)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 21)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 20)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 19)
- Harvard's drop-out Mark Zuckerberg returns to Harvard
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 18)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 17)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 16)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 15)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 14)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 13)
- Productivity Future Vision 2011
- How to delete your Facebook account forever
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 12)
- Digital Photography: A to Z (Part 11)
-
▼
November
(17)